Compositional Monoculture
Across AI Image Generation
Three Platforms. One Constraint Architecture.
Sora, MidJourney, and OpenArt Don't Have Different Compositional Systems. They Have Different Threshold Settings
Quantitative analysis of 800 images across three leading platforms reveals that compositional displacement is driven by geometric simplification, not semantic understanding. All three use the same heuristic. All three optimize for stability over sophistication.
The analysis asked: "Is the visual mass organized in rings around a center point?" It measures how geometric elements distribute outward from the frame center, comparing observed patterns against perfect radial symmetry.
This is not an aesthetic judgment but a diagnostic probe of default geometric behavior. The analysis proceeds in four steps:
Identify the subject (segmentation mask)
Measure spatial distribution (how mass spreads from center)
Calculate radial compliance (correlation with idealized radial pattern)
Classify geometric structure (dual-center, subject-dominant, field-dominant, ineligible)
The analysis reveals the geometric scaffold beneath semantic variety, the structural skeleton that determines where elements go before artistic principles are applied. We propose that text-to-image models do not approach generation with compositional neutrality. They operate within a consistent geometric prior that favors radial symmetry and central mass distribution, what we term the B0 basin, a default attractor in compositional space where the model naturally settles unless forced otherwise.
See Full Technical Analysis for MidJourney, Sora and OpenArt.
The Perfect Linear Progression: Three Parameter Settings, One Constraint Architecture
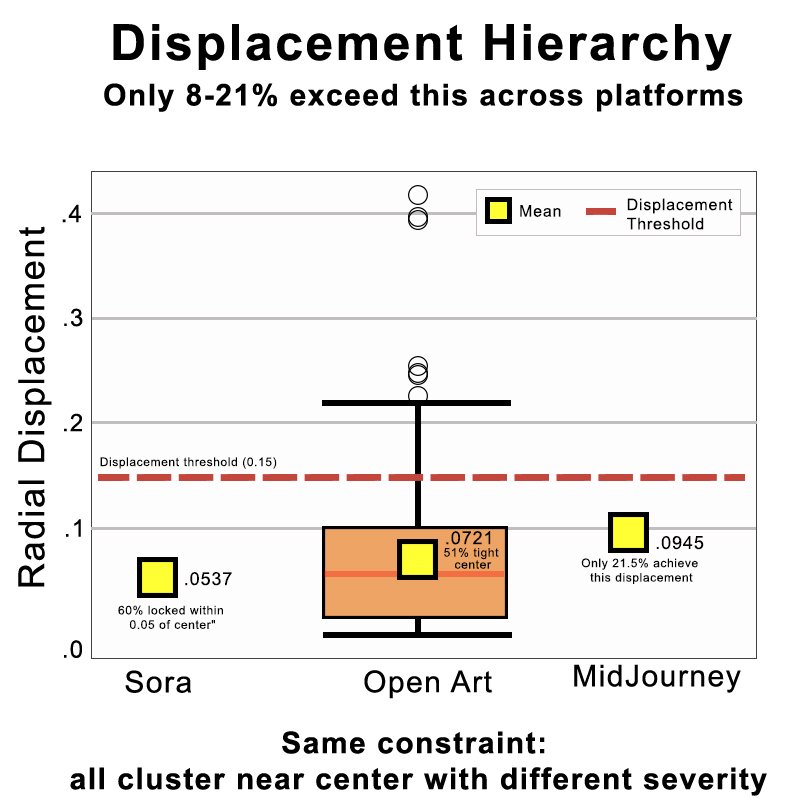
Every measured metric shows the same ordering: Sora < OpenArt < MidJourney
OpenArt sits exactly in the middle on every metric. This isn't coincidence, it's evidence of a tunable parameter within shared constraint architecture.
What is Compositional Monoculture?
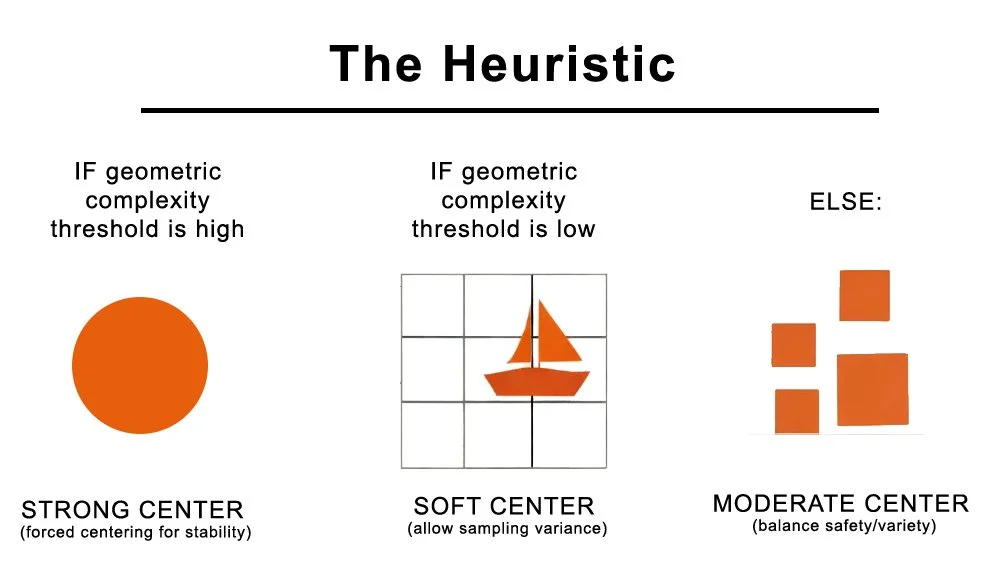
Brief explanation: Despite semantic diversity (portraits, action shots, architecture, abstracts), AI image generators produce geometrically uniform outputs. Subjects that should demand radically different compositional treatments, a centered portrait versus a dynamic action shot—instead receive similar spatial scaffolding. The models don't compose based on what they depict; they compose based on how geometrically simple the scene is.
This pattern repeats subject matter:
What is RCA-2?
(Radial Compliance Analysis)
One-sentence definition: A measurement framework that quantifies how strongly visual mass organizes in concentric rings around a center point.
The Four Steps:
Identify the subject (segmentation mask)
Measure spatial distribution (how mass spreads from center)
Calculate radial compliance (correlation with idealized radial pattern)
Classify geometric structure (dual-center, subject-dominant, field-dominant, ineligible)
What it reveals: The geometric scaffold beneath semantic variety, the structural skeleton that determines where elements go before artistic principles are applied.
RCA-2 is not an aesthetic judgment. It's a diagnostic probe revealing default geometric behavior under neutral prompting. Traditional metrics measure semantic correctness ('Did it generate a cat?'). RCA-2 measures compositional constraint ('Where did it choose to place the cat, and why?')."
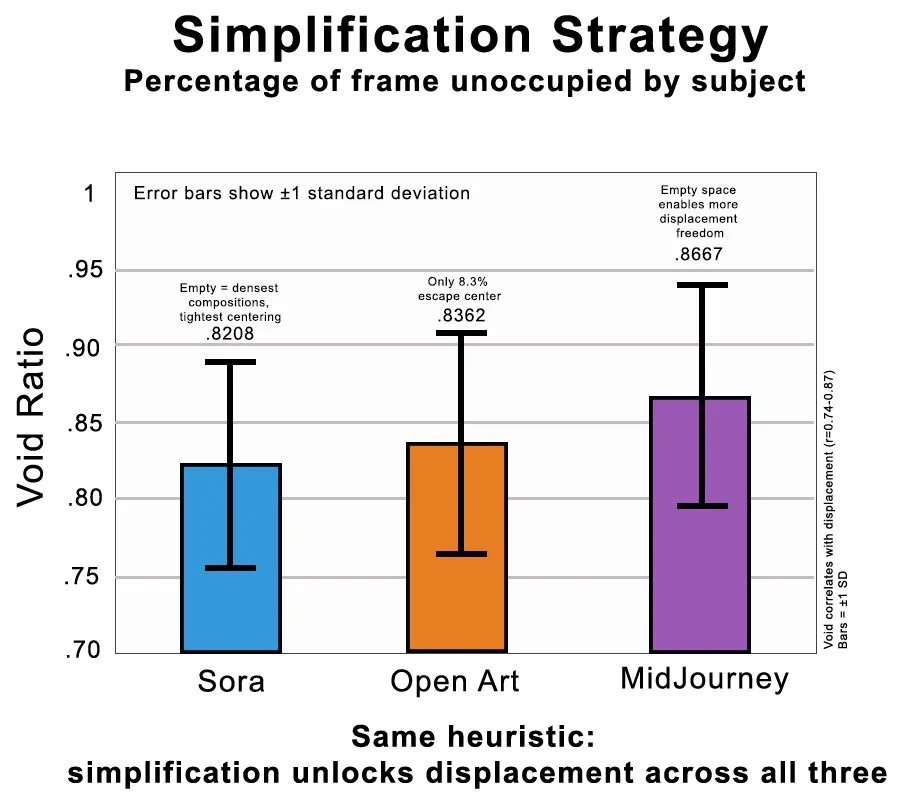
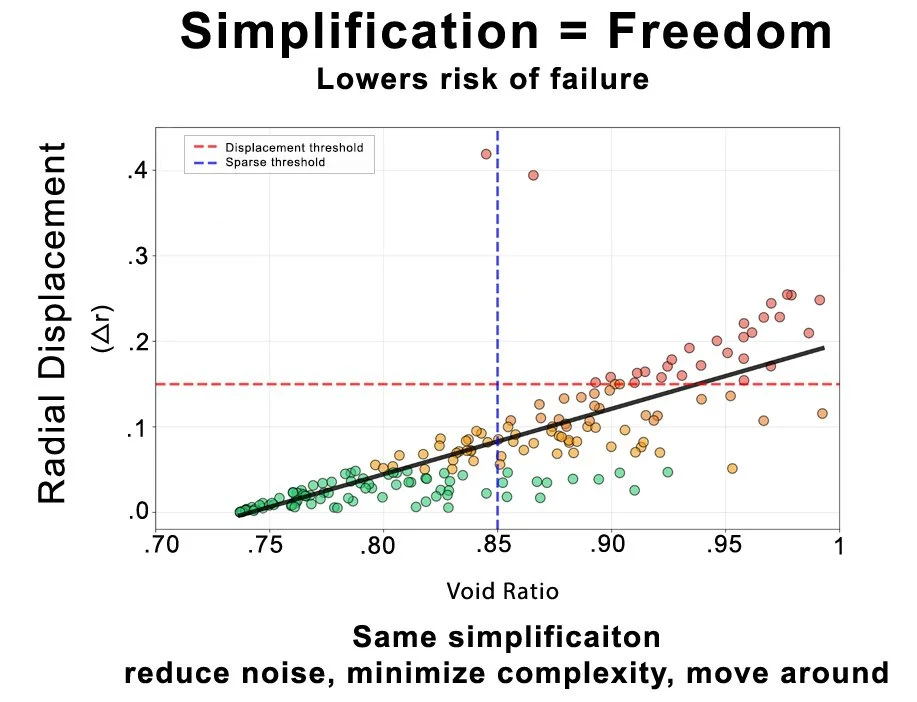
The Core Mechanism: Simplification → Wobble
The Evidence:
54.1% of OpenArt displacement explained by void ratio alone (r=0.736, p<0.0001)
74.9% of Sora displacement explained by void ratio (r=0.865) — even stronger
Sparse compositions have 3.6× more displacement than dense (p<0.0001, Cohen's d≈1.5)
What this means: Models calculate geometric complexity → determine risk → soften or enforce centering constraint accordingly. This is not semantic category recognition, compositional rule application, or artistic intelligence. It's risk mitigation through geometric calculation.
Visual recommendation: The scatter plot from page 7 showing void ratio vs displacement with the three platforms color-coded, regression lines overlaid
Vertical Bias
1.7-1.9× more Y-axis freedom than X-axis (universal to generative models)
Corner Avoidance
2-6% extreme corner occupation vs 25% if random
Dual Radial Systems
6-8× higher frame variance than mass variance (field variable, subject fixed)
Extreme Displacement
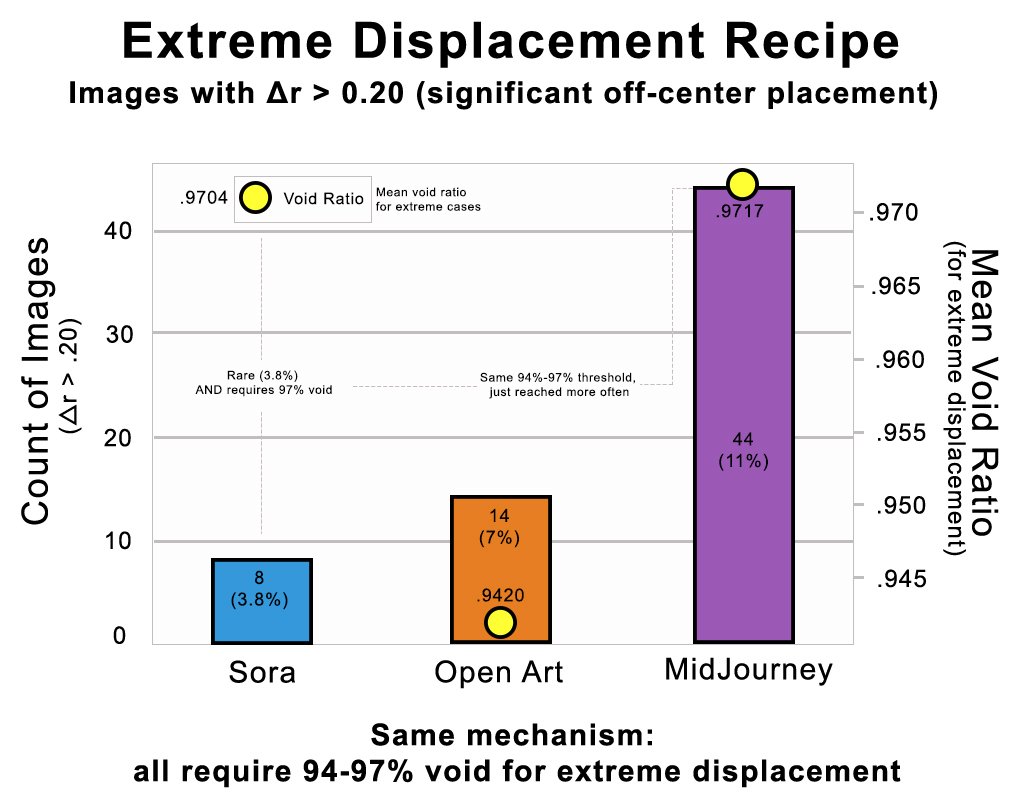
All three require 94-97% void space for Δr>0.20
Architectural Ceilings Sora: 0.28 | OpenArt: 0.42 | MidJourney: 0.56 (overcome through prompting)
For AI Companies
Current optimization objectives (preference ratings, reconstruction loss, stability) actively select against compositional sophistication. Centered compositions with high void ratios represent computational equilibria satisfying all objectives simultaneously—they're the path of least resistance.
The challenge: "Good" and "compositionally appropriate" are orthogonal under current training regimes.
For Researchers
Measurement infrastructure now exists. What was previously observable only qualitatively ("AI art looks samey") is now quantifiable:
Correlation strength (r=0.736)
Effect size (Cohen's d≈1.5)
Basin depth (51% within 0.05 of center)
Architectural ceiling (Δr max = 0.42)
RCA-2 enables:
Cross-architecture comparison
Progress measurement toward compositional diversity
Architectural diagnosis beyond semantic correctness
Identification of intervention points
For Product Teams
Users requesting "extreme off-center" compositions will hit invisible walls. These aren't soft preferences—they're hard architectural limits. The displacement ceilings (0.28 / 0.42 / 0.56) represent physical constraints that would require architectural changes to overcome.
User impact: Prompting strategies are fighting geometric safety heuristics, not lack of understanding. No amount of prompt engineering escapes the basin without adversarial techniques.
Note: It is important to reinforce that radial and centered compositions are neither incorrect nor undesirable; they are widely used in human visual practice. The issue identified here is not the presence of these structures, but their persistence as a default, limiting the geometric range explored across otherwise diverse outputs. That we have focused a lot on semantic identification, but not compositional intelligence in both training and reward behaviors.
The Evidence: Three Comprehensive Studies
MidJourney: The Loosest Enforcement
400 images analyzed
39% locked within 0.05 of center
Similar simplification heuristic (r=0.738, R²=0.545)
Architectural ceiling: 0.56
Sora: The Strictest Enforcement
200 images analyzed
60% locked within 0.05 of center
Strongest simplification heuristic (r=0.865, R²=0.749)
Architectural ceiling: 0.28
200 images analyzed
51% locked within 0.05 of center
Moderate simplification heuristic (r=0.736, R²=0.541)
Architectural ceiling: 0.42
Study Design
Dataset: 100 identical prompts across 8 semantic categories (Animals, People, Nature, Architecture, Abstract, Objects, Seasonal, Underwater/Sky)
Why identical prompts? To isolate architectural behavior from prompt variation. Same semantic input → different geometric outputs reveals platform-specific constraint thresholds.
Sample size: 800 total images (200 Sora, 200 OpenArt, 400 MidJourney)
Analysis period: January 2025
Framework: Radial Compliance Analysis (RCA-2) measuring displacement (Δr), void ratio (rᵥ), compactness, isotropy, and radial compliance (RC)
Statistical rigor: Pearson correlations, t-tests with effect sizes (Cohen's d), significance testing (p-values), distribution analysis (KDE, CDF, percentiles)
Key Insights at a Glance
12.8% of sparse images still lock to center. The heuristic softens constraints but doesn't eliminate them. Displacement emerges from sampling variance when constraint weakens—it's probabilistic permission, not compositional intelligence.
The dancer achieving RC=0.68 (top 3%) with perfect centering and high void space isn't a success story—it's Exhibit A for why optimization metrics are orthogonal to compositional appropriateness.
Perfect center occurs at LESS sparsity (0.75 void) and MORE compactness (0.96) than average. The model has learned multiple 'safe' configurations: compact blob at moderate void is safer than extreme simplification.
Sora uses void ratio MORE deterministically (r=0.865) than OpenArt (r=0.736), not less. The difference is threshold height, not mechanism strength.
What Comes Next?
For researchers: RCA-2 provides falsifiable predictions testable on other platforms . The simplification heuristic is an architectural hypothesis that can be confirmed or refuted with empirical measurement.
For developers: Escaping monoculture requires:
Explicit compositional reasoning modules (not pattern matching)
Training objectives beyond preference (compositional sophistication)
Architectural changes (not just parameter tuning)
Separation of "stable" from "good" in optimization
For the field: This work demonstrates that compositional constraint is measurable, quantifiable, and comparable across architectures. You cannot improve what you cannot measure. Now we can measure it.